Drivers Of Land Use Change Definition
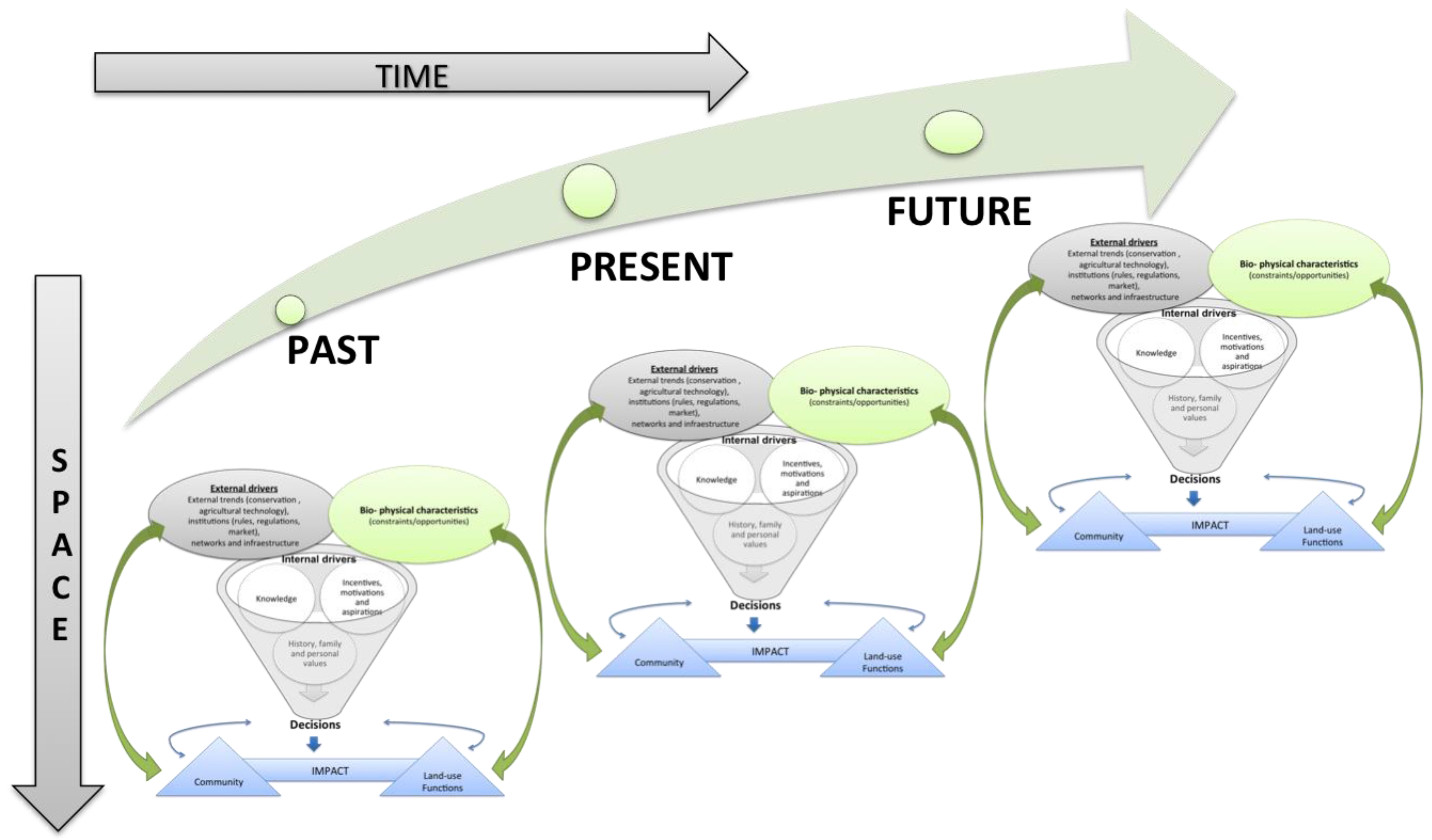
Identifying drivers of land use change. FRA definition (FAO 2013): The conversion of forest to other land use or the long-term reduction of the tree. Land Use, Land-Use Change, and Forestry The phrase 'land-use change and forestry' was used in discussions leading up to the Protocol as the name for a 'sector/source category.' It is also used as the title of a chapter in the IPCC Guidelines. Land use changes and socio-economic drivers David M. Class description definition Our definition Other definitions Interface. And change in land use.
Understanding and analysis of drivers of land-use and -cover change (LUCC) is a requisite to reduce and manage impacts and consequences of LUCC. The aim of the present study is to analyze drivers of LUCC in Southern Mexico and to see how these are used by different conceptual and methodological approaches for generating transition potential maps and how this influences the effectiveness to produce reliable LUCC models. Spatial factors were tested for their relation to main LUCC processes, and their importance as drivers for the periods 1993–2002 and 2002–2007 was evaluated by hierarchical partitioning analysis and logistic regression models.
Tested variables included environmental and biophysical variables, location measures of infrastructure and of existing land use, fragmentation, and demographic and social variables. The most important factors show a marked persistence over time: deforestation is mainly driven by the distance of existing land uses; degradation and regeneration by the distance of existing disturbed forests. Nevertheless, the overall number of important factors decreases slightly for the second period. These drivers were used to produce transition potential maps calibrated with the 1993–2002 data by two different approaches: (1) weights of evidence (WoE) to represent the probabilities of dominant change processes, namely deforestation, forest degradation, and forest regeneration for temperate and tropical forests and (2) logistic RM that show the suitability regarding the different land-use and -cover (LUC) classes. Maintype 6 0 Seriale. Validation of the transition potential maps with the 2002–2007 data indicates a low precision with large differences between LUCC processes and methods. Areas of change evaluated by difference in potential showed that WoE produce transition potential maps that are more accurate for predicting LUCC than those produced with RM.